Causes and consequences of climate change – the role of the financial services industry
Abstract: This article examines the causes and consequences of climate change, focusing on the significant role of the financial services industry. Climate change, driven by greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and industrial activities, leads to severe environmental, economic, and social impacts, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and biodiversity loss. The financial services industry contributes to climate change through investments in fossil fuels and high-emission sectors but also holds the potential to drive positive change through sustainable finance initiatives. By adopting green bonds, ESG investing, and adhering to regulatory policies, financial institutions can help mitigate climate impacts. The article highlights the challenges and opportunities in the transition to sustainable finance, emphasizing the need for robust ESG data, regulatory clarity, and stakeholder alignment. Through case studies and supporting data, it illustrates how early adopters of sustainable practices can gain a competitive edge and contribute to a low-carbon economy. The article concludes with a call to action for financial institutions to embrace sustainability, recognizing their crucial role in securing a safer and more equitable future.

Introduction
The world has witnessed increasingly frequent and severe climate-related events, from devastating hurricanes to record-breaking heatwaves. One of the most recent example is Dubai. In mid-April 2024, Dubai recorded more than 250mm of rain in less than 24 hours, exceeding all records in daily rainfall in the last 75 years. The United Arabian Emirates averages 140-200 mm of rainfall per year, while Dubai typically receives only 97mm. Overall, the monthly average for April based on historic data is only about 8mm. As a consequence, the city of Dubai faced a flash flood and hundreds of flights were cancelled.
These events underscore the urgent need to address climate change, a challenge that is intricately linked to human activities and the global economy. This article explores the causes and consequences of climate change, with a particular focus on the pivotal role of the financial services industry.
Understanding the causes of Climate Change
Definition and Background
Climate change refers to significant and lasting changes in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. The current phase of climate change, characterized by global warming, is largely driven by human activities since the Industrial Revolution.
Primary causes of Climate Change
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The combustion of fossil fuels for energy and transportation is the primary source of carbon dioxide (CO2), a leading greenhouse gas. Other significant greenhouse gases include methane (CH4), emitted from agricultural practices and landfills, and nitrous oxide (N2O) from industrial activities.
Deforestation and Land Use Changes
The clearing of forests for agriculture, urban development, and other purposes reduces the number of trees that can absorb CO2. This process not only increases atmospheric CO2 levels but also disrupts local ecosystems.
Industrial Activities and Fossil Fuel Dependency
Industries, particularly those reliant on fossil fuels, contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. The production of cement, steel, and chemicals involves processes that release substantial amounts of CO2.
Supporting Data
Graphs and charts illustrating the rise in global temperatures and greenhouse gas emissions highlight the alarming trends. For example, data from NASA and NOAA show a consistent increase in global temperatures over the past century, correlating strongly with rising CO2 levels. Additionally, case studies from the energy, transportation, and agriculture sectors illustrate the major contributions of these industries to greenhouse gas emissions.
Consequences of Climate Change
Environmental Impact
Rising Sea Levels
Melting polar ice caps and glaciers contribute to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities worldwide. This phenomenon results in increased flooding, erosion, and habitat loss for marine and coastal species.

Source: NASA.org, accessed 27.05.2024, https://climate.nasa.gov
Extreme Weather Events
The frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires, have escalated. These events cause widespread destruction, displacing communities and overwhelming disaster response systems.
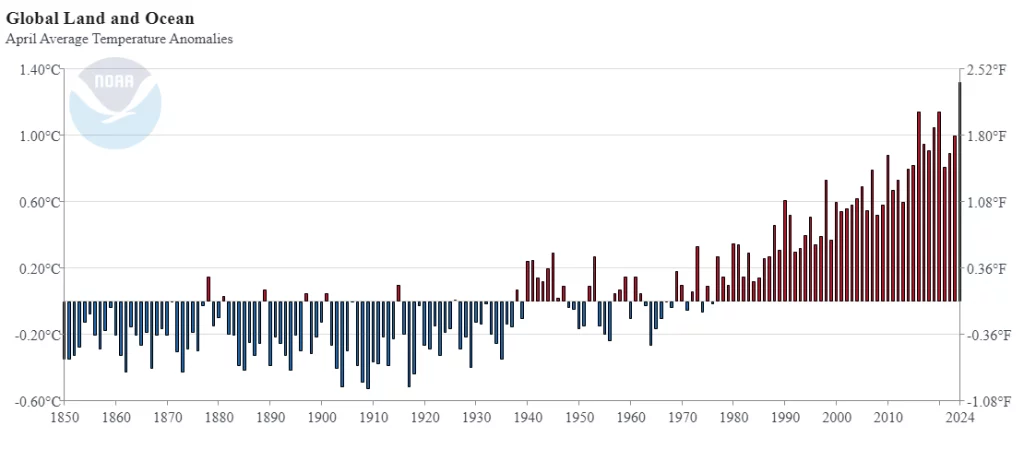
Source: ncei.org, accessed 27.05.2024, https://ncei.noaa.gov
Loss of Biodiversity
Climate change disrupts ecosystems, leading to the extinction of species unable to adapt to rapidly changing conditions. Coral reefs, for example, are highly susceptible to ocean warming and acidification, resulting in mass bleaching events.

Source: Living Planet Index, accessed 27.05.2024, https://livingplanetindex.org
Economic Impact
Damage to Infrastructure and Property
Climate-related disasters cause billions of dollars in damage each year. Hurricanes, floods, and wildfires destroy homes, businesses, and infrastructure, necessitating costly repairs and rebuilding efforts.
Impact on Agriculture and Food Security
Changing weather patterns affect crop yields and livestock production, threatening food security. Droughts and floods can devastate agricultural areas, leading to food shortages and increased prices.
Costs related to Health and Disaster Response
The health impacts of climate change include heat-related illnesses, respiratory problems from wildfire smoke, and the spread of vector-borne diseases. Additionally, the financial burden on healthcare systems and disaster response efforts continues to grow.
Social Impact
Displacement of Populations
Climate change forces people to leave their homes due to rising sea levels, extreme weather, and loss of livelihoods. These climate refugees often face uncertain futures and strain on resources in receiving areas.
Health Risks
Heatwaves, poor air quality, and changing patterns of infectious diseases pose significant health risks. Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly and children, are particularly at risk.
Social Inequality exacerbated by Climate Change
The impacts of climate change disproportionately affect low-income and marginalized communities. These groups often have fewer resources to adapt and recover, exacerbating existing social inequalities. According to a study of the World Bank, the consequences of climate change may push an additional 132 million people into extreme poverty by 2030 (source: The World Bank).
The Role of the Financial Services Industry
Contribution to Climate Change
Financial institutions have historically funded fossil fuel projects and high-emission industries, contributing to the continued reliance on these energy sources. These investments support infrastructure that locks in high carbon emissions for decades. From an internal perspective, the financial sector’s operations, including office energy use, travel, and data centers, also contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. While these may seem minor compared to industrial emissions, they add up across the global industry.
Furthermore, the Financial Services Industry manages the wealth of private persons, corporations and pension fund schemes. By selecting appropriate investments such as funds and stocks, the financial services industry is allocating capital to the underlying companies. These activities direct the money flow either to companies which contribute significantly to climate change (e.g. oil and gas companies) or to companies which support the green transition (e.g. solar panel manufacturer).
Shifting Towards Sustainability
In response to growing awareness and regulatory pressure, many financial institutions are adopting sustainable finance practices. Green bonds, which fund environmentally friendly projects, and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing, which integrates sustainability into investment decisions, are gaining traction.
Additionally, governments and international bodies are implementing policies to encourage sustainable finance. The European Union’s Sustainable Finance Action Plan, for example, aims to reorient capital flows towards sustainable investment and manage financial risks from climate change with major initiatives such as the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR).
Several financial institutions are setting examples in sustainable finance. For instance, HSBC has committed to providing $100 billion in sustainable financing and investment by 2025. Similarly, BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager, has emphasized the importance of sustainability in its investment approach.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
The transition to sustainable finance is not without challenges. Financial institutions face regulatory uncertainty, the need for robust ESG data, and potential short-term financial trade-offs. Additionally, aligning all stakeholders, including clients and shareholders, with sustainability goals can be complex.
Opportunities
Despite these challenges, the shift towards sustainable finance presents significant opportunities. There is a growing market for green financial products, and early adopters can gain a competitive edge. Innovation in green technologies and sustainable business models can drive long-term profitability.
Supporting data and information
Data on investment trends in sustainable vs. non-sustainable sectors illustrate the growing emphasis on sustainability. According to the Global Sustainable Investment Alliance, sustainable investing assets reached $35.3 trillion in 2020, representing 36% of all professionally managed assets globally. Examples of financial policies impacting climate action highlight how regulation can drive change in the industry.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
In summary, climate change is driven by human activities, particularly greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes. The consequences are far-reaching, affecting the environment, economy, and society. The financial services industry plays a critical role in both contributing to and mitigating climate change.
Shifting Towards Sustainability
Addressing climate change is an urgent priority that requires collective action from all sectors of society. The financial services industry, with its significant influence and resources, has the potential to be a powerful force for positive change. By embracing sustainability, this industry can help secure a safer and more equitable future for all.

